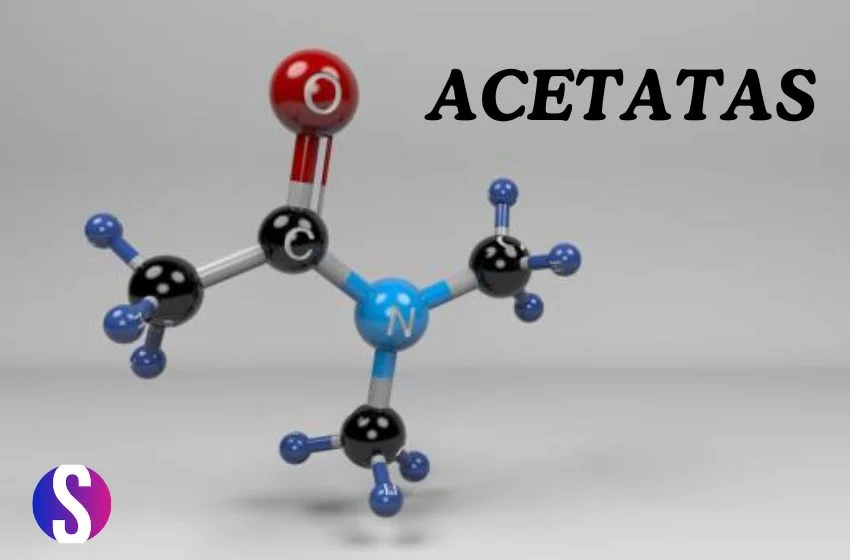
Acetates, a family of organic compounds, have found widespread applications in various industries due to their unique properties and versatility. This article delves into the world of acetates, exploring their chemical structure, production methods, and diverse applications.
Chemical Structure and Types of Acetates
Acetates are characterized by the presence of an acetate group, which consists of a carbonyl group (C=O) bonded to a methyl group (CH3). This functional group gives acetates their distinctive properties and reactivity.
There are several types of acetates, each with its own specific characteristics:
- Inorganic acetates: These compounds are formed by the reaction of acetic acid with inorganic bases. Examples include sodium acetate, potassium acetate, and ammonium acetate.
- Organic acetates: Organic acetates are derived from the reaction of acetic acid with alcohols. They are classified based on the type of alcohol used:
- Alkyl acetates: These are formed from the reaction of acetic acid with primary or secondary alcohols. Examples include ethyl acetate, methyl acetate, and isopropyl acetate.
- Aryl acetates: These are formed from the reaction of acetic acid with phenols. Examples include phenyl acetate and benzyl acetate.
- Glyceryl acetates: These are formed from the reaction of acetic acid with glycerol. Examples include monoglycerides and diglycerides.
Production of Acetates
Acetates are primarily produced through two methods:
- Fermentation: This is a biological process that involves the conversion of sugars or carbohydrates into acetic acid by microorganisms. The resulting acetic acid is then reacted with alcohols or bases to produce acetates.
- Chemical synthesis: Acetates can also be synthesized chemically through various reactions, such as the reaction of acetic anhydride with alcohols or the reaction of acetic acid with alkyl halides.
Applications of Acetates
Acetates have a wide range of applications across various industries:
1. Food and Beverage Industry:
- Flavoring agent: Acetates, especially ethyl acetate, are used as flavoring agents in many food products, including candies, baked goods, and beverages.
- Preservative: Some acetates, such as sodium acetate, can act as preservatives in certain food products.
- Solvent: Acetates can be used as solvents in food processing and extraction.
2. Pharmaceutical Industry:
- Drug intermediates: Acetates are often used as intermediates in the synthesis of pharmaceuticals.
- Excipients: Acetates can be used as excipients in drug formulations to improve their solubility, stability, or bioavailability.
- Solvents: Acetates can be used as solvents in the production of pharmaceutical products.
3. Chemical Industry:
- Solvents: Acetates are excellent solvents for a wide range of substances, including paints, coatings, adhesives, and cleaning products.
- Reagents: Acetates are used as reagents in various chemical reactions, such as esterification and acetylation.
- Plasticizers: Some acetates, such as cellulose acetate, can be used as plasticizers to improve the flexibility of plastics.
4. Textile Industry:
- Dyeing: Acetates can be used as solvents in the dyeing of textiles.
- Textile finishing: Acetates can be used in textile finishing processes to improve the properties of fabrics.
5. Other Applications:
- Photography: Acetates can be used in the production of photographic films and papers.
- Cosmetics: Acetates can be found in various cosmetic products, such as nail polish and hairspray.
- Electronics: Acetates can be used in the production of electronic components and devices.
Safety and Environmental Considerations
While acetates are generally considered safe when used properly, it is important to handle them with care. Some acetates can be flammable or irritating, and inhalation or ingestion can be harmful. Proper safety measures, such as wearing protective equipment and avoiding exposure, should always be followed.
In terms of environmental impact, acetates are generally biodegradable and do not pose significant risks to the environment when used and disposed of responsibly. However, it is still important to minimize waste and avoid pollution.
In conclusion,
Acetates are versatile compounds with a wide range of applications across various industries. Their unique properties, including their solubility, stability, and reactivity, make them valuable in fields such as food, pharmaceuticals, chemicals, textiles, and more. By understanding the chemistry and applications of acetates, we can appreciate their importance in our daily lives and continue to explore new and innovative uses for this valuable class of compounds.